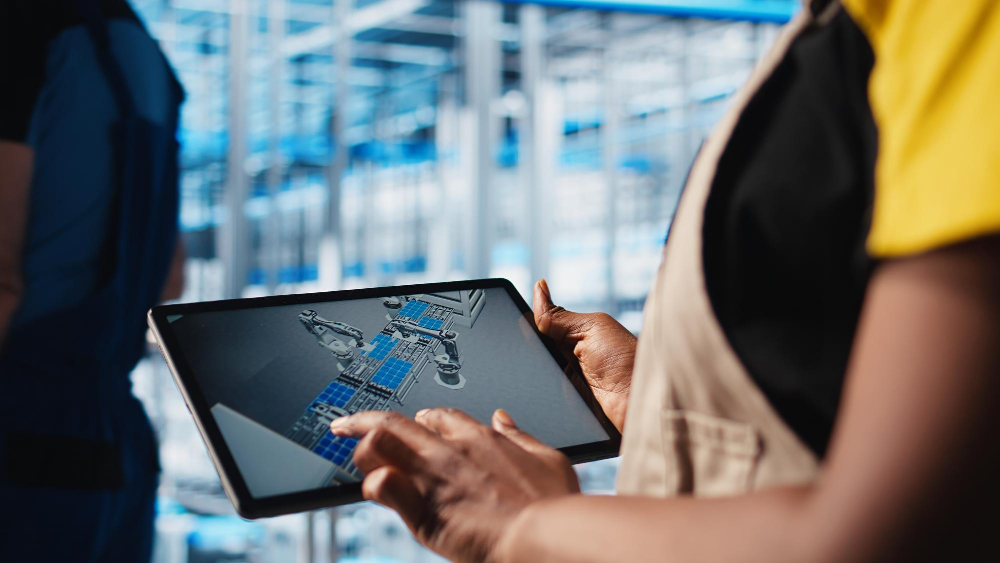
In the rapidly evolving world of Industry 4.0, digital twins have emerged as one of the most transformative technologies shaping the next generation of manufacturing and logistics. The fundamental concept behind a digital twin is simple, yet its implications are revolutionary. A digital twin is a virtual representation of a physical asset, system, or process, continuously updated with real-time data. This digital mirror enables companies to visualize, simulate, predict, and optimize how a physical entity performs under various conditions—without the risks or costs of trial and error in the real world.
Digital twins bridge the gap between the physical and digital realms, merging Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, big data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) into one integrated ecosystem. They act as a continuously learning digital counterpart that evolves as its physical counterpart does, reflecting even the smallest operational changes.
For example, a manufacturer can create a digital twin of a factory floor—complete with real-time data from machines, production lines, and environmental factors. Engineers and managers can then simulate production runs, test how process adjustments might impact efficiency, or detect early signs of equipment failure. Similarly, in logistics, a digital twin can represent an entire supply chain network, tracking every shipment, vehicle, and warehouse to identify potential bottlenecks before they happen.
This ability to see, predict, and control physical operations through a virtual environment offers organizations an unprecedented level of visibility and intelligence. The digital twin concept, once confined to advanced aerospace and automotive sectors, is now being adopted across multiple industries thanks to falling sensor costs, growing cloud computing capacity, and advancements in data analytics platforms.
The rise of digital twins is not just a passing technology trend—it’s a major step toward the intelligent, data-driven enterprise. Manufacturers and logistics providers are under increasing pressure to optimize efficiency, improve product quality, reduce downtime, and respond rapidly to shifting market demands. Digital twins enable them to achieve these goals through predictive and prescriptive capabilities that deliver actionable insights in real time.
1. Predictive Maintenance and Reduced Downtime
One of the most valuable uses of digital twins is in predictive maintenance. By continuously monitoring equipment through sensors and feeding performance data into its digital model, organizations can detect anomalies long before they lead to critical failures. Predictive algorithms can estimate when a machine will need maintenance, allowing companies to schedule repairs proactively and minimize costly unplanned downtime. This not only extends the lifespan of equipment but also enhances worker safety and operational continuity.
2. Process Optimization and Quality Improvement
Digital twins allow companies to experiment with process parameters in a virtual environment before implementing them physically. This means that manufacturers can test how different materials, workflows, or layouts affect performance, efficiency, and quality—without halting production. By analyzing the outcomes across multiple simulations, production teams can identify the most effective configurations and optimize resource allocation, resulting in consistent product quality and reduced waste.
3. Intelligent Supply Chain Management
In logistics and supply chain operations, digital twins are becoming crucial to enhancing visibility and agility. A supply chain digital twin integrates live data from suppliers, transportation routes, warehouses, and customer demand into a single dynamic model. With this, companies can anticipate disruptions, evaluate “what-if” scenarios, and make data-driven decisions instantly. Whether it’s rerouting shipments due to weather or adjusting inventory to match forecasted demand, the digital twin empowers logistics teams to act proactively rather than reactively.
4. Enabling Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Environmental sustainability has become a central focus for industries worldwide. Digital twins help organizations track energy consumption, emissions, and resource utilization at granular levels. By simulating alternative production methods or logistics routes, companies can minimize waste, reduce carbon emissions, and achieve sustainability goals while maintaining profitability. The insights derived from these models make it easier to align operational strategies with environmental compliance standards.
5. Workforce Empowerment and Knowledge Transfer
Another important yet often overlooked benefit is how digital twins empower the workforce. Engineers, operators, and planners can interact with virtual models to gain deeper insights into complex systems, making data-centric decision-making more intuitive. Additionally, digital twin environments can be used for immersive training—boosting skills development and aiding knowledge transfer across teams. This capability becomes particularly valuable as organizations navigate talent shortages and the need for continuous upskilling in the face of technological transformation.
Looking Ahead: The Path to a Fully Connected Enterprise
The future of digital twins lies in their increasing integration across enterprise systems. As artificial intelligence, edge computing, and 5G connectivity become more widespread, digital twins will evolve from isolated applications into collaborative ecosystems that mirror entire manufacturing and logistics networks. These interconnected twins will communicate with each other—allowing end-to-end visibility from product design and production to distribution and customer use.
In the coming years, the ability to create self-optimizing, data-rich digital ecosystems will define the most competitive industrial organizations. Companies that adopt digital twins early are already gaining measurable advantages—greater operational resilience, faster innovation, and stronger customer satisfaction through ultra-responsive, intelligent supply chains.